Answers
Answer:
The answer to your question is given below.
Explanation:
Aluminium has atomic number of 13. Thus, the electronic configuration of aluminium can be written as:
Al (13) —› 1s² 2s²2p⁶ 3s²3p¹
The orbital diagram is shown on the attached photo.
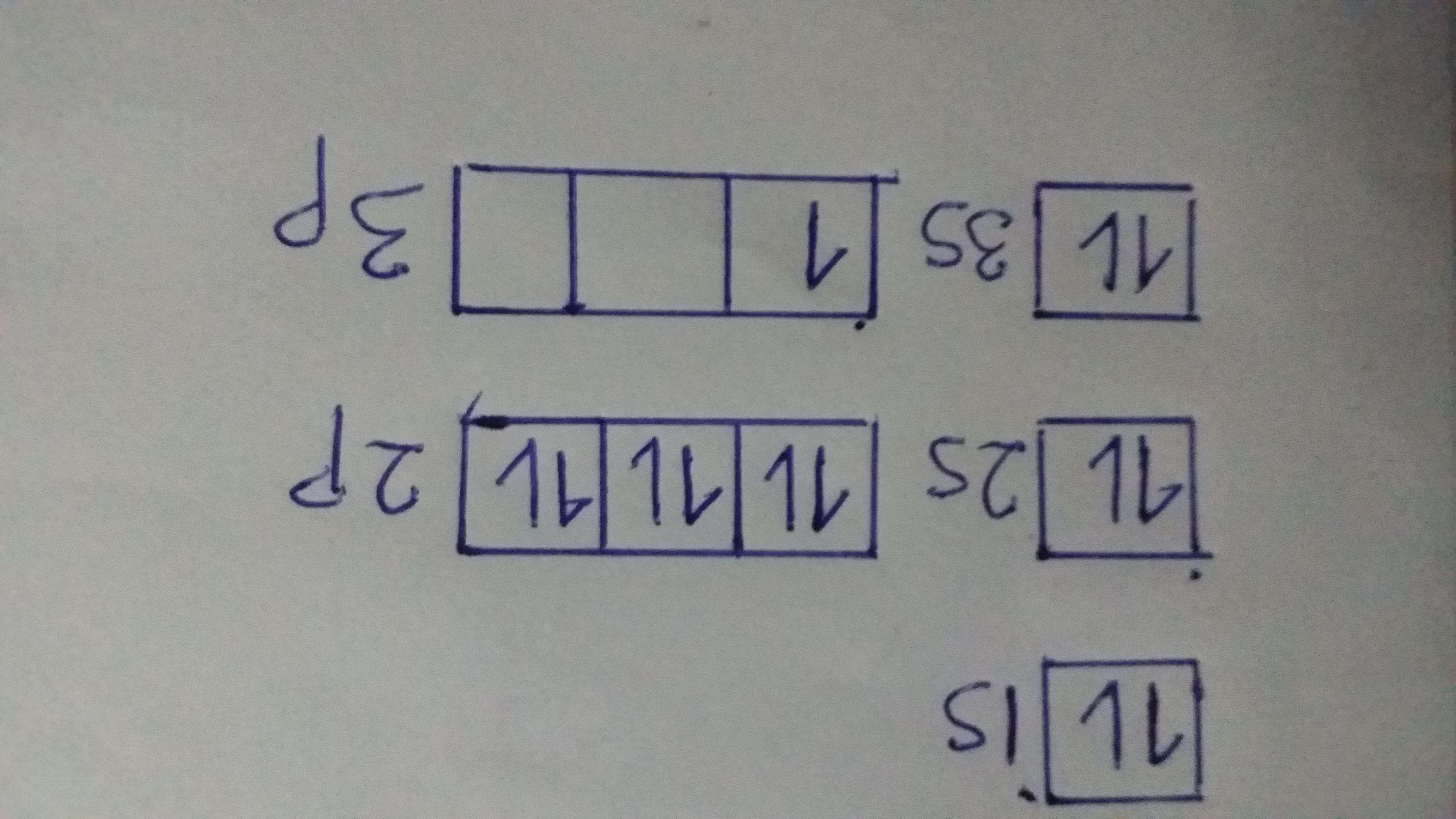
Answer: screen shot
Explanation:

Related Questions
When a solution is diluted with water, the ratio of the initial to final
volumes of solution is equal to the ratio of final to initial molarities
Select one:
True
-
Answers
The correct answer for this problem would be TRUE.
Explanation: it is true that when a solution is diluted with water, the ratio of the initial to final volumes of solution is equal to the ratio of final to initial molarities.
When a solution is diluted with water, the ratio of the initial to final volumes of solution is equal to the ratio of final to initial molarities. The statement is True.
Concentration refers to the amount of a substance in a defined space. Another definition is that concentration is the ratio of solute in a solution to either solvent or total solution.
There are various methods of expressing the concentration of a solution.
Concentrations are usually expressed in terms of molarity, defined as the number of moles of solute in 1 L of solution.
Solutions of known concentration can be prepared either by dissolving a known mass of solute in a solvent and diluting to a desired final volume or by diluting the appropriate volume of a more concentrated solution (a stock solution) to the desired final volume.
Learn more about Concentrations, here:
https://brainly.com/question/10725862
#SPJ3
Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5720 years and this is a fast-order reaction. If a piece of wood has converted 75 % of the carbon-14, then how old is it?
Answers
Answer:
11445.8years
Explanation:
Half-life of carbon-14 = 5720 years
First we have to calculate the rate constant, we use the formula :
How many mL of calcium hydroxide are required to neutralize 25.0 mL of 0.50 M
nitric acid?
Answers
Answer:
6.5 mL
Explanation:
Step 1: Write the balanced reaction
Ca(OH)₂ + 2 HNO₃ ⇒ Ca(NO₃)₂ + 2 H₂O
Step 2: Calculate the reacting moles of nitric acid
25.0 mL of 0.50 M nitric acid react.
[tex]0.0250L \times \frac{0.50mol}{L} = 0.013 mol[/tex]
Step 3: Calculate the reacting moles of calcium hydroxide
The molar ratio of Ca(OH)₂ to HNO₃ is 1:2. The reacting moles of Ca(OH)₂ are 1/2 × 0.013 mol = 6.5 × 10⁻³ mol
Step 4: Calculate the volume of calcium hydroxide
To answer this, we need the concentration of calcium hydroxide. Since the data is missing, let's suppose it is 1.0 M.
[tex]6.5 \times 10^{-3} mol \times \frac{1,000mL}{1.0mol} = 6.5 mL[/tex]
Complete ionic equation K2CO3(aq)+2CuF(aq) → Cu2CO3(s)+2KF(aq) Examine each of the chemical species involved to determine the ions that would be present in solution. Be sure to consider both the coefficients and subscripts of the molecular equation, and then write this precipitation reaction in the form of a balanced complete ionic equation. Express your answer as a chemical equation including phases.
Answers
Answer:
2K+(aq) + CO3²¯(aq) + Ca^2+(aq) + 2F¯(aq) —› Cu2CO3(s) + 2K+(aq) + 2F¯(aq)
Explanation:
K2CO3(aq) + 2CuF(aq) → Cu2CO3(s) + 2KF(aq)
The complete ionic equation for the above equation can be written as follow:
In solution, K2CO3 and CuF will dissociate as follow:
K2CO3(aq) —› 2K+(aq) + CO3²¯(aq)
CuF(aq) —› Ca^2+(aq) + 2F¯(aq)
Thus, we can write the complete ionic equation for the reaction as shown below:
K2CO3(aq) + 2CuF(aq) —›
2K+(aq) + CO3²¯(aq) + Ca^2+(aq) + 2F¯(aq) —› Cu2CO3(s) + 2K+(aq) + 2F¯(aq)