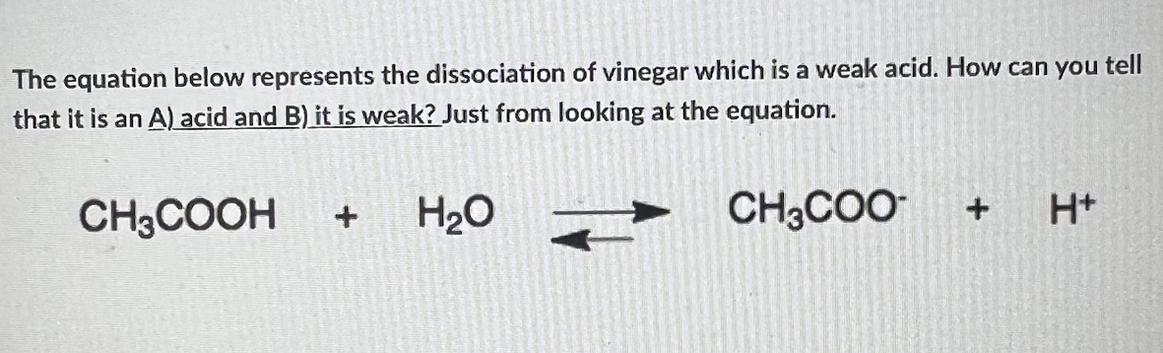
Answers
Because it is not very effective at transferring [tex]H^{+}[/tex] ions to water, vinegar is a weak acid. Less than 0.4% of the [tex]CH_{3}CO_{2}H[/tex]molecules in a 1 M solution interact with water to create [tex]H_{3}O^{+}[/tex]and [tex]CH_{3}CO_{2}^{-}[/tex] ions. More than 99.6% of the acetic acid molecules are still whole.
Weak acidsAcids that partially dissociate in solution are referred to as weak acids. To put it another way, a weak acid is any acid that is not a strong acid. A weak acid's strength is influenced by how much it dissociates; the more it dissociates, the stronger the acid.In comparison to weak acids, strong acids have a lower pH. 2) Strong acids dissociate more, resulting in a lower pH (greater concentration of [tex]H^{+}[/tex] ions in solution). 3) This can be verified by usingFor more information on weak acid kindly visit to
https://brainly.com/question/22104949
#SPJ1
Related Questions
The table shows the number of charged particles in an ion.
Charged Particles
Charge on Particle Number of Particles
Positive 3
Negative 2
A negatively charged substance is brought near the ion. What will most likely happen?
The negatively charged ion will repel the substance.
The negatively charged ion will attract the substance.
The positively charged ion will repel the substance.
The positively charged ion will attract the substance.
Answers
Answer: three
Explanation:
What happens when a solid is dissolved into a liquid?
.
Answers
40 grams of KCl are dissolved in 100 mL of water at 45C.
How many additional grams of
KCI are needed to make the solution saturated at 80 C?
Answers
40 grams of KCl are dissolved in 100 mL of water at 45C. 5g of additional grams of KCI are needed to make the solution saturated at 80 C as the solubility of KCl is 45g/ml
A uniform combination of a number of solutes within a solvent is referred to as a solution. One frequent illustration of a Solution is adding sugar cubes into your cup of tea and coffee. Solubility is the quality that makes sugar molecules more soluble.
In water, potassium chloride (KCl) dissolves. Its water solubility, like that of all other solutes, depends on temperature. The solubility of a salt increases as the solvent's temperature rises. This is fairly simple to experience with sugar. 40 grams of KCl are dissolved in 100 mL of water at 45C. 5g of additional grams of KCI are needed to make the solution saturated at 80 C as the solubility of KCl is 45g/ml.
To know more about solubility, here:
https://brainly.com/question/29661360
#SPJ1
4- Calculate the pH of 0.3 M NH, where is K = 1.7 x 10
Answers
The pH of .3 M NH, where is K = 1.7 x 10^-5 is 11.87 calculated from the equation of dissociation constant.
How can pH be determined?Kb= [A] /[A + ][X− ]
1.7×10 −5 = x ^2 /0.3
⇒x= 7.5 ×10 −3
∴[OH − ][H + ]=7.5 ×10 −3
[H + ] =10 ^−14 ⇒pH=11.87
When describing the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution, chemists use the pH scale, which is also known as acidity and previously stood for "potential of hydrogen". Greater pH values are seen in basic or alkaline solutions than acidic solutions.
Potential hydrogen is the meaning of the acronym pH, which indicates how much hydrogen is present in liquids and how active the hydrogen ion is.
As a first step, we shall ascertain the pKa of the solution before calculating its Ka. When a solution reaches the equivalence point, its pH and pKa are equal. So, by using a titration curve and the Ka = - log pKa equation, we may rapidly ascertain the value of Ka.
For more information on pH kindly visit to
https://brainly.com/question/2288405
#SPJ1
The satellite image above shows the San Francisco area along the West Coast. What feature is marked by "X"?
A. A bay
B. A fresh water lake
C. A mountain
D. A volcano
Answers
A bag because it broad inlet of the sea where the land curves inwards
Draw both enantiomers of the following compound
Answers
Enantiomers rotate the plane of polarized light in opposite directions, and this property is used to distinguish between them in a process called optical rotation.
What are the enantiomers of a compound?Enantiomers are pairs of molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
They are isomers, meaning they have the same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in their three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in space.
Enantiomers exhibit identical physical and chemical properties, except for their interaction with plane-polarized light (a type of light that oscillates in a single plane).
Learm= more about enantiomers at: https://brainly.com/question/30216513
#SPJ1
A 2.6 mol sample of N2 is held in a 4191 mL balloon at 89.9 atm. What temperature (in Celcius) is the gas at? Answer to one decimal place.
Answers
To convert to Celsius, we subtract 273.15 from the Kelvin temperature, giving us a final answer of 42.1°C.
What is temperature?Temperature is a physical quantity that measures the average kinetic energy of the particles in a system. It is an important parameter for understanding the behavior of matter and the underlying physical processes at work. Temperature is measured in units such as degrees Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F), Kelvin (K), or Rankine (°R). Temperature affects the rate at which chemical reactions occur and the movement of particles in solids, liquids, and gases.
The ideal gas law states that PV = nRT,
where n is the number of moles,
P is the pressure,
V is the volume, R is the ideal gas constant (8.314 J/molK), and
T is the temperature in Kelvin.
Rearranging the equation, we get T = (PV)/(nR).
Plugging in our values, we get T = (89.9 atm * 4191 mL)/(2.6 mol * 8.314 J/molK) = 115.2 K.
To convert to Celsius, we subtract 273.15 from the Kelvin temperature, giving us a final answer of 42.1°C.
To learn more about temperature
https://brainly.com/question/27988898
#SPJ1
CHALLENGE The circles below represent of the large circle, and multiply it by 30. That Earth and the moon. Measure the diameter would be the correct distance from Earth to the moon at this scale. Draw the two circles in the space provided. Use the correct distance you found.● = Earth ●=moon
Answers
To draw the two circles, we would need to draw a smaller circle with a diameter of 2,532.5 miles (representing the moon) and a larger circle with a diameter of 75,974.4 miles (representing the Earth) that is 30 times larger than the smaller circle.
What is the explanation for the above response?If we assume that the larger circle represents the Earth, then the diameter of the Earth would be 30 times the diameter of the smaller circle representing the moon. Let's say that the diameter of the smaller circle is x. Then the diameter of the larger circle (Earth) would be 30 times x or 30x.
To find the correct distance from Earth to the moon at this scale, we need to know the actual distance from Earth to the moon, which is approximately 238,855 miles or 384,400 kilometers. If we divide this distance by the scale factor of 30, we get:
238,855 miles / 30 = 7,961.8 miles
Therefore, the diameter of the smaller circle (moon) would be approximately 7,961.8 miles / π = 2,532.5 miles (rounded to one decimal place). And the diameter of the larger circle (Earth) would be 30 times that or 75,974.4 miles
So, to draw the two circles, we would need to draw a smaller circle with a diameter of 2,532.5 miles (representing the moon) and a larger circle with a diameter of 75,974.4 miles (representing the Earth) that is 30 times larger than the smaller circle.
Learn more about Earth at:
https://brainly.com/question/19581790
#SPJ1
When you balance the equation Ca(OH)₂ + H₃PO₄ ---> Ca₃(PO₄)₂ + H₂O, what is the coefficient of calcium phosphate?
a.)
1
b.)
3
c.)
2
d.)
6
Answers
The answer is A --------
The oxides SO2 and N2O5 will form what acids?
Answers
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3
N2O5, on the other hand, reacts with water to form nitric acid (HNO3), which is a strong acid. The reaction can be represented as follows:
N2O5 + H2O → 2HNO3
Therefore, SO2 forms sulfurous acid (H2SO3) and N2O5 forms nitric acid (HNO3) when they react with water.
2AI + 6HCI=2AlCl3 + 3H₂
3. Aluminum reacts with HCI to produce aluminum chloride (AICI3) and hydrogen gas (H₂).
Calculate the number of moles of HCI required to react with 0.62 moles of Al.
Answers
3.0 moles of [tex]Al[/tex] can fully react with hydrogen chloride to produce 4.5 moles of [tex]H_{2}[/tex]. Thus, 0.93 moles will be produced by 0.62 moles of [tex]Al[/tex].
STOICHIOMETRYBased on this inquiry, how does aluminum react with hydrogen chloride to produce aluminum chloride and hydrogen gas[tex]Al +6HCl= AlCl_{3} +3H_{2}[/tex]According to this equation, 3 moles of hydrogen gas are produced during the reaction of 2 moles of aluminum ([tex]Al[/tex]).As a result, 3 moles of aluminum will result in 3 3 2 = 4.5 moles of hydrogen gas.As a result, the entire reaction of 3.0 moles of [tex]Al[/tex]with hydrogen chloride can produce 4.5 moles of [tex]H_{2}[/tex].The proportion of reactants to products before, during, and after chemical processes is known as stoichiometry.For more information on stoichiometry kindly visit to
https://brainly.com/question/19484482
#SPJ1
Question 5(Multiple Choice Worth 3 points)
(07.02 LC)
The substances below are listed by increasing specific heat capacity value. Starting at 30.0 °C, they each absorb 100 kJ of thermal energy. Which one do you expect to increase in temperature the least?
a) Cadmium, 0.230 J/(g °C)
b) Sodium, 1.21 J/(g °C)
c) Water, 4.184 J/(g °C)
d) Hydrogen, 14.267 J/(g °C)
Answers
Component form of the vector v is as follows: 4 3 1.5 1 Using the standard basis vectors I and j), express the vector w as follows: 3 two 1 4 pp . 1 3 w 3.5 C. V plus w= d. Determine the vector v's magnitude
What does "vector" mean?
Latin word for "carrier" is "vector." Point A is transported to point B by vectors. The orientation of the vectors AB is the direction in which point A is moved in relation to point B, and the amplitude of the vector is the width of the line connecting the two locations A and B. The terms Euclidean vectors and spatial vectors are also used to refer to vectors.
A vector space is what?
A vector space, also known as a linear space, is a collection of things called vectors that can be added to and multiplied ("scaled") by figures called scalars in the fields of mathematics, physics, and engineering.
To know more about vector visit:
https://brainly.com/question/27854247
#SPJ1
Please help me
Define acid.
Mention four products of destructive distillation of coal.
In a tabular, highlight two differences between diamond and graphite.
List four types of salt.
Outline two physical properties of a base.
Answers
4. acidic salt, basic salt, neutral salt, and double salt
I only know the two questions not the rest sorry
Liquid octane CH3CH26CH3 will react with gaseous oxygen O2 to produce gaseous carbon dioxide CO2 and gaseous water H2O. Suppose 6.9 g of octane is mixed with 42.2 g of oxygen. Calculate the maximum mass of carbon dioxide that could be produced by the chemical reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
Answers
The maximum mass of carbon dioxide that could be produced from 6.9 g of octane and 42.2 g of oxygen is 21.3 g, rounded to 2 significant digits.
What is Octane?
Octane is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula [tex]C_{8} H_{18}[/tex] It is an organic compound belonging to the alkane group, which means it consists of only carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms bonded together by single covalent bonds. Octane is a colorless liquid with a molecular weight of approximately 114 g/mol and is commonly used as a component in gasoline or fuel for internal combustion engines.
From the balanced equation, we know that 1 mole of octane reacts with 12.5 moles of oxygen to produce 8 moles of carbon dioxide. Therefore, 0.0605 mol of octane would require 0.0605 mol x 12.5 = 0.75625 mol of oxygen to fully react.
Since we have only 1.32 mol of oxygen, which is in excess compared to the 0.75625 mol required by octane, oxygen is the excess reactant, and octane is the limiting reactant.
Now, we can use the stoichiometry of octane to carbon dioxide to calculate the maximum mass of carbon dioxide produced:
From the balanced equation, we know that 1 mole of octane produces 8 moles of carbon dioxide.
Molar mass of carbon dioxide (CO2) = 44.01 g/mol
Maximum moles of carbon dioxide produced from octane = 0.0605 mol x 8 = 0.484 mol
Maximum mass of carbon dioxide produced from octane = 0.484 mol x 44.01 g/mol = 21.3 g
Remember to round the final answer to 2 significant digits as requested.
Learn more about Octane from the given link
https://brainly.com/question/28469125
#SPJ1
What is true of spontaneous reactions?
O They are indicated by a negative change in Gibbs free energy.
O They have a positive value of AS.
O They are instantaneous.
O They always release heat.
Help 20pts
Answers
Explanation: Spontaneous reactions are those that occur without any external input of energy. A negative change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) indicates that a reaction is spontaneous. The other options do not always hold true for spontaneous reactions. The value of entropy change (ΔS) can be positive or negative, spontaneous reactions are not necessarily instantaneous, and they do not always release heat.
The isotope Tl-208 undergoes β decay with a half-life of 3.1 min.
What is the decay constant for this process?
a.)
4.47 min⁻¹
b.)
2.15 min⁻¹
c.)
0.224 min⁻¹
d.)
0.031 min⁻¹
Answers
The decay constant for this process is
c.) 0.224 min⁻¹How to find the decay constantThe decay constant (λ) is related to the half-life (t1/2) by the following equation:
λ = ln(2) / t1/2
where
ln(2) is the natural logarithm of 2, which is approximately 0.693.
Substituting the given half-life of 3.1 min into the equation, we get:
λ = ln(2) / (3.1 min) ≈ 0.223 min^(-1)
Therefore, the decay constant for the β decay of Tl-208 is approximately 0.223 min^(-1).
Learn more about decay constant at
https://brainly.com/question/12699719
#SPJ1
2. A student prepared a 0.500 M solution of an unknown acid, and measured the pH as 3.56 at 25°C. (a) What is the acid dissociation constant of this unknown acid? (b) What percentage of acid is ionised in this solution
Answers
To solve this problem, we can use the following equation that relates the pH of a solution to the acid dissociation constant (Ka) and the concentration of the acid:
pH = -log[H+]
where [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution.
(a) To find the Ka of the unknown acid, we need to first find the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution. We can do this by taking the inverse of the pH and converting it to a concentration:
[H+] = 10^(-pH) = 10^(-3.56) = 2.17 × 10^(-4) M
What is the acid dissociation constant of this unknown acid?The acid dissociation constant (Ka) can then be calculated using the equation:
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]
where [A-] is the concentration of the conjugate base of the acid and [HA] is the concentration of the undissociated acid. Since we don't know the values of these concentrations, we need to use the fact that the solution is 0.500 M to make an assumption about the degree of dissociation (α) of the acid:
α = [A-]/[HA]
Since the solution is not extremely dilute, we can assume that the degree of dissociation is small and that the concentration of the undissociated acid is approximately equal to the initial concentration of the acid. Therefore, we can write:
[A-] ≈ 0.500α
[HA] ≈ 0.500 - 0.500α
Substituting these expressions into the equation for Ka, we get:
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA] ≈ ([H+][A-])/0.500α
≈ ([H+]/Ka)(0.500α)/(1-α)
Solving for Ka, we get:
Ka ≈ H+/0.500α
Substituting the values we have calculated, we get:
Ka ≈ (2.17 × 10^(-4))(1-α)/(0.500α) = 4.37 × 10^(-5)
Therefore, the acid dissociation constant of the unknown acid is approximately 4.37 × 10^(-5).
(b) To find the percentage of acid that is ionized in the solution, we can use the equation:
α = [A-]/[HA] = 10^(-pKa + pH)/(1 + 10^(-pKa + pH))
where pKa is the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant. Substituting the values we have calculated, we get:
α = 10^(-(-4.36) + 3.56)/(1 + 10^(-(-4.36) + 3.56)) ≈ 0.008
Therefore, the percentage of acid that is ionized in the solution is approximately 0.8%.
Learn more about dissociation constant from
https://brainly.com/question/30930515
#SPJ1
To solve this problem, we can use the following equation that relates the pH of a solution to the acid dissociation constant (Ka) and the concentration of the acid:
pH = -log[H+]
where [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution.
(a) To find the Ka of the unknown acid, we need to first find the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution. We can do this by taking the inverse of the pH and converting it to a concentration:
[H+] = 10^(-pH) = 10^(-3.56) = 2.17 × 10^(-4) M
What is the acid dissociation constant of this unknown acid?The acid dissociation constant (Ka) can then be calculated using the equation:
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]
where [A-] is the concentration of the conjugate base of the acid and [HA] is the concentration of the undissociated acid. Since we don't know the values of these concentrations, we need to use the fact that the solution is 0.500 M to make an assumption about the degree of dissociation (α) of the acid:
α = [A-]/[HA]
Since the solution is not extremely dilute, we can assume that the degree of dissociation is small and that the concentration of the undissociated acid is approximately equal to the initial concentration of the acid. Therefore, we can write:
[A-] ≈ 0.500α
[HA] ≈ 0.500 - 0.500α
Substituting these expressions into the equation for Ka, we get:
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA] ≈ ([H+][A-])/0.500α
≈ ([H+]/Ka)(0.500α)/(1-α)
Solving for Ka, we get:
Ka ≈ H+/0.500α
Substituting the values we have calculated, we get:
Ka ≈ (2.17 × 10^(-4))(1-α)/(0.500α) = 4.37 × 10^(-5)
Therefore, the acid dissociation constant of the unknown acid is approximately 4.37 × 10^(-5).
(b) To find the percentage of acid that is ionized in the solution, we can use the equation:
α = [A-]/[HA] = 10^(-pKa + pH)/(1 + 10^(-pKa + pH))
where pKa is the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant. Substituting the values we have calculated, we get:
α = 10^(-(-4.36) + 3.56)/(1 + 10^(-(-4.36) + 3.56)) ≈ 0.008
Therefore, the percentage of acid that is ionized in the solution is approximately 0.8%.
Learn more about dissociation constant from
brainly.com/question/30930515
#SPJ1
If the volume of a gas at -40°C is double to 80 L what is the final temperature in degrees Celsius?
Answers
The final temperature is -160°C
To solve this problemWe can use the combined gas law, which relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas:
(P₁V₁)/T₁ = (P₂V₂)/T₂
Where
P₁, V₁, and T₁ are the initial pressure, volume, and temperature of the gas, and P₂, V₂, and T₂ are the final pressure, volume, and temperature of the gasIn this case, we can assume that the pressure of the gas is constant, since it is not given in the problem statement. So we can simplify the equation to:
(V₁/T₁) = (V₂/T₂)
Where
V₁ and T₁ are the initial volume and temperature V₂ and T₂ are the final volume and temperatureWe are given that the initial volume (V₁) is 80 L and the final volume (V₂) is twice that, or 160 L. We are also given that the initial temperature (T₁) is -40°C. To find the final temperature (T₂), we can plug these values into the equation:
(V₁/T₁) = (V₂/T₂)
(80 L)/(-40°C) = (160 L)/T₂
Simplifying:
-2 L/°C = (160 L)/T₂
Multiplying both sides by -1°C/2 L (the reciprocal of -2 L/°C):
1/2 = (T₂)/(160 L) x (-1°C/2 L)
1/2 = -T₂/320
Multiplying both sides by -1 to isolate T₂:
-1/2 = T₂/320
T₂ = -160°C
Therefore, the final temperature is -160°C.
Learn more about combined gas law here : brainly.com/question/11296079
#SPJ1
What is the Molality of a solution in which
25 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 2.0
kg of water?
Answers
The molality of a solution is determined by the amount of solute (in moles) and the mass of the solvent (in kilograms). To convert the mass of NaCl to moles, the molar mass of NaCl is 58.44 g/mol. The number of moles of NaCl is 25 g / 58.44 g/mol = 0.427 mol. The molality of the solution is 0.213 mol/kg.
What is molality?The amount of a solute dissolved in a solvent is indicated by the chemical term "molality," which is commonly defined in terms of moles of solute per kilogramme of solvent. Because it takes into account variations in the volume of the solution owing to temperature and pressure, it differs from molarity, which quantifies the quantity of a solute in moles per litre of solution.
To calculate the molality of a solution, we need to know the amount of solute (in moles) and the mass of the solvent (in kilograms).
In this case, we are given:
Mass of solute (NaCl) = 25 g
Mass of solvent (water) = 2.0 kg
To calculate the amount of solute in moles, we need to convert the mass of NaCl to moles using its molar mass:
Molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g/mol
Number of moles of NaCl = (25 g) / (58.44 g/mol) = 0.427 mol
Now we can calculate the molality of the solution:
Molality = (number of moles of solute) / (mass of solvent in kg)
Molality = (0.427 mol) / (2.0 kg) = 0.213 mol/kg
Therefore, the molality of the solution is 0.213 mol/kg.
To know more about molality, visit
brainly.com/question/26921570
#SPJ1
At 25 ∘C
, the equilibrium partial pressures for the reaction
A(g)+2B(g)↽−−⇀C(g)+D(g)
were found to be A=5.63
atm, B=5.00
atm, C=5.47
atm, and D=5.63
atm.
What is the standard change in Gibbs free energy of this reaction at 25 ∘C
?
Answers
The standard change in Gibbs free energy of the reaction at 25 ∘C is -1.69 kJ/mol.
What is standard change?
To find the standard change in Gibbs free energy of the reaction, we need to use the following equation:
ΔG° = -RT ln(K)
where ΔG° is the standard change in Gibbs free energy, R is the gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K), T is the temperature in Kelvin (25 °C = 298 K), and K is the equilibrium constant.
To find K, we need to use the equilibrium partial pressures:
K = (PC × PD) / (PA × PB²)
where PA, PB, PC, and PD are the equilibrium partial pressures of A, B, C, and D, respectively.
Substituting the values, we get:
K = (5.47 atm × 5.63 atm) / (5.63 atm × (5.00 atm)²)
K = 0.6176
Now we can calculate the standard change in Gibbs free energy:
ΔG° = -RT ln(K)
ΔG° = -(8.314 J/mol·K) × (298 K) × ln(0.6176)
ΔG° = -1,690 J/mol or -1.69 kJ/mol
Therefore, the standard change in Gibbs free energy of the reaction at 25 ∘C is -1.69 kJ/mol.
What is free energy?
Free energy, also known as Gibbs free energy, is a thermodynamic quantity that represents the amount of energy in a system that is available to do work at a constant temperature and pressure. It is denoted by the symbol G and is expressed in units of joules (J) or calories (cal).
In simple terms, free energy is the energy that can be used to do work. It is defined by the equation:
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
where ΔH is the change in enthalpy (heat content) of the system, ΔS is the change in entropy (disorder) of the system, and T is the absolute temperature in Kelvin.
If ΔG is negative, the reaction is spontaneous and can proceed without the input of external energy. If ΔG is positive, the reaction is non-spontaneous and requires energy input to proceed. If ΔG is zero, the system is at equilibrium.
To know more about free energy, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/14150518
#SPJ1
Can someone help me with this I am too lazy to work it out
Answers
Answer:
acid +metal ----->salt +hydrogen
20. Calculate the mole fractions (X) of each compound in each of the following solutions:
a. 19.4 g of H2SO4 in 0.251 L of H20 (density of water is 1.00 g/mL)
b.35.7 g of KBr in 16.2 g of water
C.233 g of CO2 in 0.409 L of water
Answers
[tex]CO_{2}[/tex]The following compounds' mole fractions (X) are (a)0.986 (b)0.750 (c)0.811 for the given solutions.
How can the mole fraction of 19.4 g of H2SO4 in 0.251 L of water be determined?[tex]H_{2}SO_{4}[/tex] mass is 19.4 g.
[tex]H_{2}SO_{4}[/tex]'s molecular weight is 98.08 g/mol.
It's molecular weight is 19.4 g/98.08 g/mol, or 0.1979 mol.
Density times volume is 1.00 g/mL times 0.251 L and 251 g for water mass.
[tex]H_{2} O[/tex] has a molecular weight of 18.02 g/mol.
Water moles are equal to 251 g / 18.02 g/mol, or 13.93 mol.
The solution's total moles are equal to 0.1979 mol plus 13.93 mol, or 14.13 mol.
Sulphuric Acid's mole fraction is equal to 0.1979 mol/14.13 mol, or 0.014.
Water mole fraction is equal to 13.93 mol / 14.13 mol, or 0.986 mol.
How can the mole fraction of 35.7 g of KBr in 16.2 g of water be determined?KBr's mass is 35.7 g.
KBr has a molecular weight of 119 g/mol.
The formula for KBr is 35.7 g/119 g/mol, which equals 0.300 mol.
16.2 g of water in mass
Water has a molecular weight of 18.02 g/mol.
Water moles are equal to 16.2 g / 18.02 g/mol, or 0.899 mol.
The solution has a total of 1.199 moles (0.300 mol + 0.899 mol).
The mole fraction of KBr is equal to 0.300 mol/1.199 mol, or 0.250
Water mole fraction is equal to 0.899 mol / 1.199 mol, or 0.750 moles.
How can the mole fraction of 233 g of CO2 in 0.409 L of water be determined?[tex]CO_{2}[/tex] mass = 233 g
It has a molecular weight of 44.01 g/mol.
Its moles are equal to 233 g / 44.01 g/mol, or 5.291 mol.
Water volume equals 0.409 L.
Water has a molecular weight of 18.02 g/mol.
(density × volume) / molecular weight (1.00 g/mL 409 mL) / 18.02 g/mol = 22.71 mol = number of moles of water
The solution's total moles are equal to 5.291 mol plus 22.71 mol, or 28.00 mol.
[tex]CO_{2}[/tex] mole fraction = 5.291 moles / 28.00 moles = 0.189
[tex]H_{2} O[/tex] mole fraction is 22.71 mol/28.00 mol, or 0.811 moles.
To learn more about mole fraction visit:
brainly.com/question/29808190
#SPJ9
Which of the following represents beta decay
OA. Tc-TC+y
O B.
B. 14Gd→ 144Sm+ He
O C. 160Eu+e→ 169 Sm
62
O D.
D.
63
164Gd→ ¹6 Tb + e
160
65
Answers
The correct answer that represents beta decay is
D. 164Gd → 164Tb + e, What happens in beta decayIn beta decay, a neutron in the nucleus is converted into a proton, and an electron (or beta particle) and an antineutrino are emitted from the nucleus.
In this case, a neutron in the 164Gd nucleus is converted into a proton, and an electron is emitted from the nucleus, resulting in the production of 164Tb.
Option A is not a valid representation of any known type of radioactive decay.
Option B represents alpha decay, in which an alpha particle is emitted from the nucleus.
Option C represents electron capture, in which an electron is captured by the nucleus.
Learn more about beta decay at
https://brainly.com/question/27770519
#SPJ1
pls help!!!
a compound is found to be 51.39% carbon, 8.64% hydrogen, and 39.97% nitrogen. it has a molecular molar mass of 140.22 g/mol. what is the molecular formula.
show work pls!!
Answers
The molecular formula of the compound, given that it contains 51.39% carbon, 8.64% hydrogen, and 39.97% nitrogen is C₆H₁₂N₄
How do i determine the molecular formula?To obtain the molecular formula, we must first determine the empirical formula. Details on how to obtain the empirical formula is given beloww:
Carbon (C) = 51.39%Hydrogen (H) = 8.64%Nitrogen (N) = 39.97%Empirical formula =?Divide by their molar mass
C = 51.39 / 12 = 4.283
H = 8.64 / 1 = 8.64
N = 39.97 / 14 = 2.855
Divide by the smallest
C = 4.283 / 2.855 = 1.5
H = 8.64 / 2.855 = 3
N = 2.855 / 2.855 = 1
Multiply through by 2 to express in whole number
C = 1.5 × 2 = 3
H = 3 × 2 = 6
N = 1 × 2 = 2
Thus, we can conclude that the empirical formula is C₃H₆N₂
Finally, we shall determine the molecular formula. Details below
Empirical formula = C₃H₆N₂Molar mass of compound = 140.22 g/molMolecular formula =?Molecular formula = empirical × n = mass number
[C₃H₆N₂]n = 140.22
[(12×3) + (1×6) + (14×2)]n = 140.22
70n = 140.22
Divide both sides by 70
n = 140.22 / 70
n = 2
Molecular formula = [C₃H₆N₂]n
Molecular formula = [C₃H₆N₂]₂
Molecular formula = C₆H₁₂N₄
Learn more about molecular formula:
https://brainly.com/question/21568927
#SPJ1
1-A tennis ball travelling at a speed of 46 m/s with a mass of 58 g. Calculate its kinetic energy Ek=0.5mv2
2-A plane at a speed of 255 m/s with a mass of 2.15 × 105 kg. calculate its kinetic energy
3-A hot air balloon with a kinetic energy of 76 550 J and a mass of 1890 kg. Calculate its velocity
Answers
The tennis ball has a kinetic energy of around 56.8 J. The aircraft has a kinetic energy of around 4.43 x 10⁹ J. The hot air balloon travels at a speed of around 9.0 m/s.
A 750 kilogramme automobile travelling at a speed of 50.0 km/h has how much kinetic energy?How much effort must be put into slowing down a 750 kg automobile from 100 km/h to 50 km/h. We know that the of this automobile at 50.0 km/h is 72,300 Joules from the last example problem.
Ek = 0.5 x 0.058 kg x (46 m/s)²
Ek = 0.5 x 0.058 kg x 2116 m²/s²
Ek = 56.8468 J
Ek = 0.5mv²
Ek = 0.5 x 2.15 x 10⁵ kg x (255 m/s)²
Ek = 0.5 x 2.15 x 10⁵ kg x 65025 m²/s²
Ek = 4.433 x 10⁹ J
Ek = 0.5mv²
v = √(2Ek/m)
v = √(2 x 76550 J / 1890 kg)
v = √(81.011 J/kg)
v = 9.0 m/s (approx.)
To know more about energy visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/8630757
#SPJ1
What two salts have the same solubility at approximately 23 C?
Answers
Answer silver chloride (AgCl) and lead chloride (PbCl2).
Explanation:
Two salts that have the same solubility at approximately 23°C are silver chloride (AgCl) and lead chloride (PbCl2).
Both AgCl and PbCl2 have very low solubilities in water at room temperature, and their solubilities are similar at around 23°C. They are both sparingly soluble salts, meaning they dissolve only to a limited extent in water to form a saturated solution.
It's important to note that solubility can vary depending on the specific conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and presence of other substances. The solubility of salts can also be affected by factors such as pH and the presence of other ions in solution. Therefore, it's always best to consult reliable sources, such as reference tables or experimental data, for accurate solubility information at a given temperature.
Round to 2 significant
figures.
5,249
Answers
5,250. The number was rounded up from 5,249 because the last digit, 9, is greater than or equal to 5.
What is rounded up?Rounding up is a mathematical operation that involves increasing a number to its nearest whole number. It is commonly used when dealing with money, measurements, or statistics. When rounding up, the number is increased to the next highest whole number. For example, if a number is 6.7, it would be rounded up to 7. Rounding up is often used when dealing with exact measurements or estimates to simplify the calculations. It can also be used to make the results of a calculation easier to understand. In the case of money, rounding up can be used to round a number to the nearest dollar. This prevents dealing with fractional amounts of money. Rounding up can also be utilized in statistical analysis, such as in the calculation of mean or median. This simplifies the data and prevents dealing with fractions or decimals.
To learn more about rounded up
https://brainly.com/question/17396482
#SPJ9
A student mixes 100. mL of 0.25 M HCl(aq) with 200. mL of 0.50 M HClO4(aq) and then dilutes the mixture with distilled water to a total volume of 500. mL. The [H3O+] in the final solution is closest to
(A) 0.0025 M
(B) 0.12 M
(C) 0.25 M
(D) 0.75 M
Answers
Answer:
The answer is B: 0.0025 M
According to molar concentration and dilution concept, the [H₃O+] in the final solution is closest to 0.05 M.
What is molar concentration?Molar concentration is defined as a measure by which concentration of chemical substances present in a solution are determined. It is defined in particular reference to solute concentration in a solution . Most commonly used unit for molar concentration is moles/liter.
The molar concentration depends on change in volume of the solution which is mainly due to thermal expansion. Molar concentration is calculated by the formula, molar concentration=mass/ molar mass ×1/volume of solution in liters.
In terms of moles, it's formula is given as molar concentration= number of moles /volume of solution in liters.In case of 2 solutions concentrated and diluted it is calculated as, M₁V₁=M₂V₂ substitution gives M₂=0.25×100/500=0.05
Learn more about molar concentration,here:
https://brainly.com/question/15532279
#SPJ2
Consider the reaction described by the chemical equation shown.
C2H4(g)+H2O(l)⟶C2H5OH(l)Δ∘rxn=−44.2 kJ
Use the data from the table of thermodynamic properties to calculate the value of Δ∘rxn
at 25.0 ∘C.
Δ∘rxn= ? J⋅K−1
Calculate Δ∘rxn.
Δ∘rxn= ? kJ
In which direction is the reaction, as written, spontaneous at 25 ∘C
and standard pressure?
reverse
both
neither
forward
Answers
The direction of the reaction, as written, spontaneous at 25 ∘C and standard pressure is reverse.
What is the direction of the reaction?
To calculate the value of Δ∘rxn at 25.0 ∘C, we can use the equation:
Δ∘rxn(T2) = Δ∘rxn(T1) + ΔH∘(products) - ΔH∘(reactants)
where;
T2 is the desired temperature (25.0 ∘C), T1 is the standard temperature (usually 25 ∘C), ΔH∘(products) is the enthalpy change of formation of the products, and ΔH∘(reactants) is the enthalpy change of formation of the reactants.Using the data from the table of thermodynamic properties, we can look up the enthalpy change of formation values for C2H4(g), H2O(l), and C2H5OH(l):
ΔH∘f(C2H4(g)) = 52.26 kJ/mol
ΔH∘f(H2O(l)) = -285.83 kJ/mol
ΔH∘f(C2H5OH(l)) = -277.69 kJ/mol
Substituting these values into the equation, we get:
Δ∘rxn(25.0 ∘C) = -44.2 kJ + (-277.69 kJ/mol) - (-52.26 kJ/mol)
Δ∘rxn(25.0 ∘C) = -44.2 kJ - (-277.69 kJ/mol) + 52.26 kJ/mol
Δ∘rxn(25.0 ∘C) = -44.2 kJ + 277.69 kJ/mol + 52.26 kJ/mol
Δ∘rxn(25.0 ∘C) = 233.23 kJ/mol
So the value of Δ∘rxn at 25.0 ∘C is 233.23 kJ/mol.
In which direction is the reaction, as written, spontaneous at 25 ∘C and standard pressure?
Since the value of Δ∘rxn at 25.0 ∘C is positive (233.23 kJ/mol), the reaction as written is not spontaneous at this temperature and standard pressure. The correct answer is "reverse."
Learn more about enthalpy change here: https://brainly.com/question/16387742
#SPJ1
In the Periodic Table below, shade all the elements for which the neutral atom has an outer electron configuration of ms2nd2, where n and m are integers, and =m+n1.
Answers
The elements that have an outer electron configuration of ms2nd2 are located in the d-block of the periodic table and include some of the transition metals and lanthanides.
What is the periodic table?To determine which elements in the periodic table have this outer electron configuration, you can look at the position of the d-block elements in the table. The d-block elements are located in the middle of the table and include the transition metals. These elements have partially filled d orbitals, which can accommodate up to 10 electrons.
Elements in the d-block with an atomic number of 21 through 30 (scandium through zinc) have an outer electron configuration of d10s2 and do not fit the ms2nd2 configuration. However, elements in the d-block with an atomic number of 39 through 48 (yttrium through cadmium) have an outer electron configuration of d10s2p1 and can have the ms2nd2 configuration by removing the single electron in the p orbital. Elements in the d-block with an atomic number of 57 through 80 (lanthanum through mercury) also have the possibility of having an outer electron configuration of ms2nd2.
Learn more about periodic table:https://brainly.com/question/11155928
#SPJ1