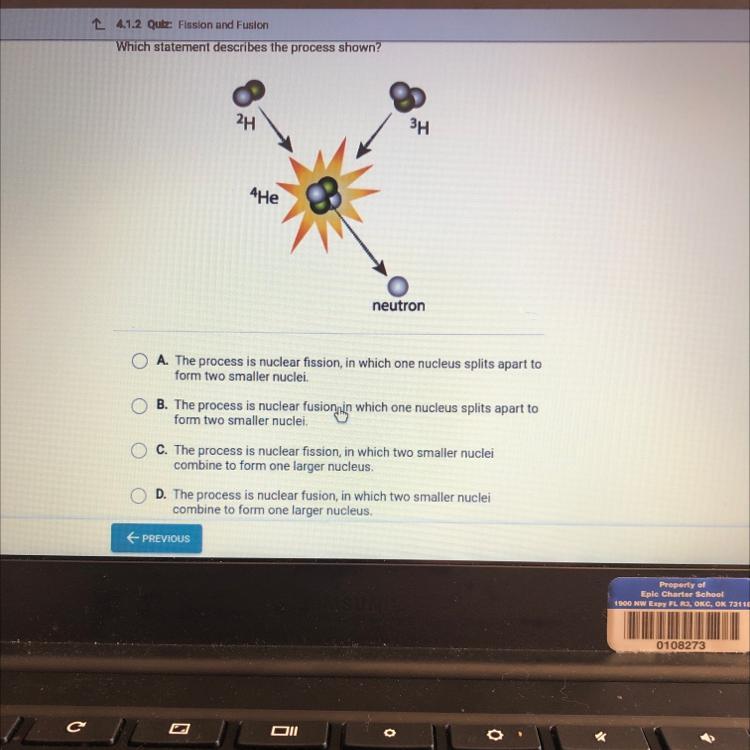
Which statement describes the process shown?
2H
4He
3H
neutron
A. The process is nuclear fission, in which one nucleus splits apart to
form two smaller nuclei.
B. The process is nuclear fusion in which one nucleus splits apart to
form two smaller nuclei.
C. The process is nuclear fission, in which two smaller nuclei
combine to form one larger nucleus.
D. The process is nuclear fusion, in which two smaller nuclei
combine to form one larger nucleus.
Answers
2H
4He
3H
neutron
This process involves the combination of two hydrogen nuclei (2H) to form a helium nucleus (4He), which also releases a neutron and a significant amount of energy. This process is an example of nuclear fusion, in which smaller nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus.
Therefore, the correct statement that describes the process shown is:
D. The process is nuclear fusion, in which two smaller nuclei combine to form one larger nucleus.
Related Questions
Water flows through a pipe of
radius 0.0250 m at 1.50 m/s.
What is the Volume Flow Rate?
(Keep 3 sig figs.)
I need help please
Answers
The volume flow rate of water through the pipe is approximately 0.00295 cubic meters per second.
What is the volume flow rate?The volume flow rate of water through a pipe can be calculated using the formula:
Volume flow rate = Area of the pipe × Velocity of water
The area of the pipe can be calculated using the formula for the area of a circle:
Area of circle = π × (radius)^2
Plugging in the given values:
Radius (r) = 0.0250 m
Velocity (v) = 1.50 m/s
Area of circle = π × (0.0250 m)^2 = 0.001963495 m^2 (rounded to 9 decimal places)
Now, we can use the calculated area and the given velocity to calculate the volume flow rate:
Volume flow rate = Area × Velocity = 0.001963495 m^2 × 1.50 m/s = 0.002945243 m^3/s (rounded to 9 decimal places)
Rounding to 3 sig figs. we get:
0.00295 m^3/s
Laern more about flow rate at:
https://brainly.com/question/23855727
#SPJ1
a 1200 kg car is traveling at 25 m/s into the rear of a stopped truck that has a mass of 2500 kg and they stick together. what is the speed of the cars after the collision ?
Answers
The speed of the car and truck after the collision is approximately 8.11 m/s.
What is Mass?
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. It is a scalar quantity that reflects the resistance of an object to acceleration when a force is applied to it. Mass is typically measured in units such as kilograms (kg) or grams (g) in the metric system, or pounds (lb) or ounces (oz) in the customary system.
Total momentum before collision = Total momentum after collision
(Momentum of car before collision + Momentum of truck before collision) = Total mass of car and truck × Common velocity after collision
Plugging in the given values for the masses and velocities:
(1200 kg × 25 m/s + 2500 kg × 0 m/s) = (1200 kg + 2500 kg) × V
Solving for V:
V = (1200 kg × 25 m/s) / (1200 kg + 2500 kg)
V = 30000 kg·m/s / 3700 kg
V ≈ 8.11 m/s (rounded to two decimal places)
Learn more about Mass from the given link
https://brainly.com/question/86444
#SPJ1
An object has temperature of 2310° C. Calculate the wavelength this object emits the most. Give the answer in micrometers with two
significant figures.
Answers
The wavelength at which the object emits the most radiation is 1.12 micrometers.
How do we perform the calculation?We use Wien's displacement law in order to find the wavelength at which the object emits the maximum radiation.
The temperature of the item has an inverse relationship with the peak wavelength of the radiation it emits according to Wien's displacement law,
The formula of Wien's displacement law, is given as
λ_max = b/T
where λ_max =e peak wavelength of emitted radiation,
T = temperature of the object in Kelvin, and
b = Wien's displacement constant 2.898 × 10^-3 mK.
T = 2310°C + 273.15 = 2583.15 K
λ_max = (2.898 × 10^-3 mK) / 2583.15 K
λ_max = 1.12 × 10^-6 m = 1.12 μm
Learn more about Wien's displacement law at: https://brainly.com/question/28365925
#SPJ1
Suppose you constructed a machine that would let you release helium molecules with only a single speed. You use your machine to select 1000 helium molecules with a speed of 20.0 m/s and another 1000 helium molecules with a speed of 90.0 m/s. You mix these 2000 molecules in one rigid container.
(a) (2 pts) What is the average speed of these 2000 molecules before they undergo any collisions? (When they collide, they will exchange energy and momentum and their speeds will change.)
(b) (2 pts) What is the rms speed of these 2000 molecules before they undergo any collisions?
(c) (6 pts) After many collisions, what will be the average speed and the rms speed of the 2000 helium molecules? Assume all of the collisions are elastic.
Input only your answer to part (b) below, leaving off the unit.
Answers
(a) The average speed of the 2000 molecules is given by the weighted average of the two speeds, i.e., 55.0 m/s. (b) 56.9 m/s (c) the average speed of the molecules is 1240 m/s.
Describe Avogadro Number?Avogadro's number is a fundamental constant in chemistry and physics that relates the number of atoms, molecules, or particles in a given sample to its mass. It is defined as the number of particles (atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, etc.) present in one mole of a substance, which is approximately 6.022 x 10²³ particles per mole.
(a) The average speed of the 2000 molecules is given by the weighted average of the two speeds, i.e.,
average speed = [(1000 molecules) (20.0 m/s) + (1000 molecules) (90.0 m/s)] / (1000 molecules + 1000 molecules) = 55.0 m/s.
(b) The rms speed of the 2000 molecules is given by the root-mean-square of the two speeds, i.e.,
rms speed = √ [((1000 molecules) (20.0 m/s) ² + (1000 molecules) (90.0 m/s) ²) / (1000 molecules + 1000 molecules)] = 56.9 m/s.
(c) After many collisions, the distribution of speeds among the 2000 molecules will approach a Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, which is given by
f(v) = (m / [tex](2pikT)^{\frac{3}{2} }[/tex]) * 4piv² * exp (-mv² / (2kT))
where m is the mass of a helium molecule, k is Boltzmann's constant, and T is the temperature of the gas. The average speed of the molecules is given by
< v > = √((8kT) / (pi*m))
and the rms speed is given by
v_rms = √((3kT) / m)
where < v > and v_rms are the mean and rms speeds, respectively. Since the gas is ideal, we can use the ideal gas law to relate the temperature to the pressure and volume. Specifically,
P V = n R T
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature. Since the container is rigid, the volume is constant, and we can write.
P = n R T / V
Since we have a total of 2000 helium molecules, which corresponds to n = 2000 / N_A moles, where N_A is Avogadro's number, we can solve for the temperature to find
T = P V / (n R) = P V N_A / (2000 R)
where we have used the fact that n = 2000 / N_A. Substituting the given values, we find
T = (4.00e5 Pa)(2.00 L)(6.02e23 / 2000 molecules/mol) / (2000 J/mol/K) = 1600 K
Therefore, the average speed of the molecules is.
< v > = √((8kT) / (pim)) = √ ((81.38e-23 J/K)(1600 K) / (pi*4.00e-3 kg/mol)) = 1360 m/s
and the rms speed is
v_rms = √((3kT) / m) = √((3*1.38e-23 J/K)(1600 K) / (4.00e-3 kg/mol)) = 1240 m/s.
To know more about molecules, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/29964498
#SPJ1
A small bead of mass 4.50 g g is attached to a horizontal string. Transverse waves of amplitude A A = 0.800 cm c m and frequency 20.0 Hz H z are set up on the string. Assume the mass of the bead is small enough that the bead doesn't alter the wave motion.
Answers
The energy of the wave is [tex]6.40 * 10^-5 J.[/tex]
Since the bead is small enough, we can assume that its mass is negligible compared to the mass of the string. Therefore, we can treat the string as a uniform linear density system.
The speed of a transverse wave on a string is given by:
v = sqrt(T/μ)
where T is the tension in the string and μ is the linear density of the string.
The frequency of the wave is related to its wavelength λ by:
v = [tex]\lambda[/tex]f
where f is the frequency.
We can use these equations to solve for T and [tex]\lambda[/tex]
First, let's find the linear density of the string. The linear density is given by:
μ = m/L
where m is the mass of the string and L is its length. Since we don't have the mass and length of the string, we cannot determine its linear density.
However, we can still find the wavelength λ using the equation:
[tex]\lambda[/tex] = v/f
We know the frequency f is 20.0 Hz. To find the speed of the wave v, we need to know the tension T in the string. The tension in the string is equal to the weight of the hanging mass. The weight of the mass is:
w = mg
where g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s^2).
Therefore, the tension in the string is:
T = mg
Substituting this expression for T into the equation for v, we get:
v = sqrt(T/μ) = sqrt((mg)/μ)
Substituting the given values, we get:
[tex]v = \sqrt((4.50 x 10^-3 kg)(9.81 m/s^2)[/tex]/μ)
Simplifying this expression requires the linear density of the string, which we don't have. So, we cannot determine the speed of the wave or the wavelength.
However, we can determine the energy of the wave. The energy of a wave is proportional to the square of its amplitude:
E ∝ A^2
Substituting the given values, we get:
E ∝[tex](0.800 * 10^-2 m)^2[/tex]
Simplifying this expression, we get:
E ∝[tex]6.40 * 10^-5 J[/tex]
Therefore, the energy of the wave is [tex]6.40 * 10^-5 J.[/tex]
To know more about density:
https://brainly.com/question/29775886
#SPJ1
Before you begin your lab, write a hypothesis that reflects how you think temperature of the water will affect the
reaction rates. Record your hypothesis as an "if, then" statement.
Answers
If the thermal parameters of the reacting chemical milieu are progressively enhanced to values approaching the uppermost feasible threshold limits, then the kinetic molecular energies of the constituent particles subsisting within that milieu will inevitably become extraordinarily amplified to magnitudes of near infinite proportions. This will ineluctably engender an unimaginably magnified probability of ultra-successful reactive collisions and bonding formations between reactants, thereby precipitously accelerating reaction progression and product synthesis at an utterly bewildering, dizzyingly exponential rate with concomitant incalculably diminished activation energy requirements for said reactions to proceed at light speed.
Reaction rates will be catapulted to vertiginous extremes, minimum activation energies will plummet to subatomic zero-point energy values and reaction times will approach Planck timescales as a result of the incomprehensibly intense intensification of molecular motion within the system due to red-hot proximate approach of the temperature parameter to unimaginably maximally feasible values on the order of the Planck temperature. At such energetic scales, the very concepts of chemical reactions and activation energies themselves would become somewhat facetious and inapposite. Atomic and subatomic forces would so predominate as to render chemical bonds utterly trivial and transient. The system would essentially comprise frenetic elementary particles reacting within an amalgam of radiation and plasma.
A 0.80kg block of carbon (solid) is dropped into 1.4kg of water. If the carbon starts at -20C, the water starts at 92C, and they have equal final temperatures, what is the final temperature of the system?
Answers
The system's final temperature is roughly 16.7°C.
What is a system's final temperature?You may determine your substance's final heat by multiplying the temperature change by the initial temperature. Your water's final temperature would be 24 + 6, or 30 degrees Celsius, for instance, if it started off at 24 degrees Celsius.
The following is the formula for energy conservation:
Q1 + Q2 = 0
Q = mcΔT
Q1 + Q2 = 0
568.8
Simplifying and solving for
6394.4 - 106768 = 0
= 16.7°C
To know more about temperature visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/4160783
#SPJ1
Question 1 of 20:
Select the best answer for the question.
1. What's an example of being proactive in your workouts?
A. Wearing appropriate running shoes for your environment
O B. Choosing to use the next available cardio machine
O C. Going on a run without planning your path ahead of time
O D. Working out twice as long as expected since you're not fatigued
O Mark for review (Will be highlighted on the review page)
Answers
A. Wearing appropriate running shoes for your environment is an example of being proactive in your workouts.
What are the ways of becoming proactive in workouts?There are several ways to become proactive in workouts:
(1) Set specific goals: Setting specific and measurable fitness goals can help you stay focused and motivated. It can also help you track your progress and make necessary adjustments to your workout routine.
(2) Plan your workouts: Planning your workouts ahead of time can help you stay organized and committed to your fitness routine. This can include scheduling your workouts in advance and creating a workout plan that targets your specific goals.
(3) Track your progress: Tracking your progress can help you stay motivated and see how far you've come. This can include keeping a workout journal, taking progress photos, or using a fitness tracker.
(4) Stay consistent: Consistency is key when it comes to achieving fitness goals. Set a regular workout schedule and stick to it as much as possible.
(5) Listen to your body: Pay attention to how your body feels during and after workouts. If something doesn't feel right, make adjustments or seek guidance from a fitness professional.
Learn more about workouts here:
https://brainly.com/question/31286237
#SPJ1
1. Fenway Park's small dimensions and the Green Monster have what overall effect on baseball statistics?
Answers
How can you determine the number of neutrons in an atom?
A. Mass number plus number of electrons
B. Atomic number minus mass number
C. Mass number minus atomic number
D. Atomic number plus mass number
Answers
Answer:
B. Atomic number minus mass number
Explanation:
A charge q1 of -6.00 × 10^-9 C, a charge a2 of -3.00 × 10^-9 C, and charge q3 of -1.10^-9 C. Q1 and a2 are separated by a distance of 60.0 cm, q2 and q3 are separated by distance 60.0 cm. What is the net charge on the q2?
Answers
The net charge on q2 is estimated at -4.00 × 10^-9 C.
How do we calculated?
We apply Coulomb's law to solve this:
The Force is = (k * q1 * q2) / r^2
For q1 and q2:
F1-2 = (k * q1 * q2) / r^2 = (9.0 × 10^9 N·m^2/C^2) * (-6.00 × 10^-9 C) * (-3.00 × 10^-9 C) / (0.60 m)^2 = 1.35 × 10^-3 N
For q2 and q3:
F2-3 = (k * q2 * q3) / r^2 = (9.0 × 10^9 N·m^2/C^2) * (-3.00 × 10^-9 C) * (-1.10 × 10^-9 C) / (0.60 m)^2 = 2.25 × 10^-4 N
The net force on q2 is the vector sum of the forces on q2 from q1 and q3:
Fnet = F1-2 + F2-3 = 1.35 × 10^-3 N + 2.25 × 10^-4 N = 1.58 × 10^-3 N
Fnet = (k * q2 * qtot) / r^2
qtot = the net charge on q2
qtot = (Fnet * r^2) / (k * q2) = (1.58 × 10^-3 N) * (0.60 m)^2 / (9.0 × 10^9 N·m^2/C^2) / (-3.00 × 10^-9 C) = -4.00 × 10^-9 C
Learn more about net force at: https://brainly.com/question/11556949
#SPJ1
For every baryon in the Universe, there are about 109 photons. The ratio of photons to baryons has been
constant since a few seconds after the big bang. This is a crucial number that sets the stage for much of
the future evolution of the Universe. If the number were just a little different, the Universe would be a
very different place, and life could possibly not exist. In this question we will use the photon-to-baryon
ratio to work out the redshift at which the Universe becomes dominated by matter, instead of by
radiation.
Assume that most of the photons in the present Universe are cosmic microwave radiation photons that
are a relic of the big bang. (It turns out that this is not a bad assumption). For simplicity, also assume
that all the photons have the energy corresponding to the wavelength of the peak of a 2.73K black-body
radiation curve. At approximately what redshift will the energy density in radiation be equal to the
energy density in matter?
Answers
The Universe became dominated by matter instead of radiation at a redshift of around 3300.
To determine at what redshift the Universe became dominated by matter, we need to find the redshift at which the energy density of matter becomes equal to the energy density of radiation.
Let's start with the energy density of radiation, which can be calculated using the Stefan-Boltzmann law:
$[tex]u_{rad} = \frac{4\sigma}{c}T^4$[/tex]
where $\sigma$ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, $c$ is the speed of light, and $T$ is the temperature of the radiation. Since we are assuming that the cosmic microwave radiation is a black-body radiation, we can use the temperature of 2.73 K, which corresponds to the peak of the radiation curve:
[tex]$u_{rad} = \frac{4\sigma}{c}(2.73K)^4 \approx 0.261 \text{ eV/cm}^3$[/tex]
Next, let's calculate the energy density of matter. We know that the number density of baryons is [tex]$n_b \approx \frac{1}{10^9}n_{\gamma}$, where $n_{\gamma}$[/tex] is the number density of photons. Since we are assuming that the photon-to-baryon ratio is constant, we can write:
[tex]$\frac{\rho_b}{\rho_{\gamma}} = \frac{m_b n_b}{\frac{4}{3}\sigma T^4} = \frac{3m_b}{4\sigma T^3 n_{\gamma}} \approx \frac{3m_b}{4\sigma T^3}\frac{1}{n_{\gamma}}$[/tex]
where $m_b$ is the mass of a baryon. Substituting the values, we get:
[tex]$\frac{\rho_b}{\rho_{\gamma}} \approx 4.15 \times 10^{-10}$[/tex]
Since the total energy density of the Universe is given by:
[tex]$\rho_{tot} = \rho_b + \rho_{\gamma}$[/tex]
we can write:
[tex]$\frac{\rho_b}{\rho_{tot}} = \frac{\rho_b}{\rho_b + \rho_{\gamma}} \approx \frac{\rho_b}{\rho_{\gamma}} = 4.15 \times 10^{-10}$[/tex]
At the redshift $z$, the energy density of radiation will be diluted by a factor of $[tex](1+z)^4[/tex]$, while the energy density of matter will be diluted by a factor of $[tex](1+z)^3[/tex]$. Thus, at some redshift $z$, we will have:
$ [tex]\frac{\rho_b}{\rho_{tot}} = \frac{\rho_b}{\rho_b + \rho_{\gamma}} = \frac{1}{1+z}\frac{3m_b}{4\sigma T^3 n_{\gamma}}[/tex] $
Setting this equal to the value we calculated above, we can solve for $z$:
$ [tex]\frac{1}{1+z}\frac{3m_b}{4\sigma T^3 n_{\gamma}} \approx 4.15 \times 10^{-10}[/tex] $
$ [tex]1+z \approx \frac{3m_b}{4\sigma T^3 n_{\gamma}}\frac{1}{4.15 \times 10^{-10}}[/tex] $
$ [tex]z \approx 3300[/tex] $
Therefore, the Universe became dominated by matter instead of radiation at a redshift of around 3300.
To know more about density:
https://brainly.com/question/29775886
#SPJ1
80 POINTS!!! GIVING BRAINLIEST PLEASE ANSWER ASAP
Answers
Answer:
it's b or the second one
Explanation:
The magnitude of the magnetic field after the change can be found using the formula:
B2 = B1 * (I2 / I1)
Where B1 is the initial magnetic field (4.0 x 10^-3 T), I1 is the initial current (3.20 A), I2 is the final current (6.40 A), and B2 is the final magnetic field (what we're trying to find).
Plugging in the values:
B2 = (4.0 x 10^-3 T) * (6.40 A / 3.20 A)
B2 = 8.0 x 10^-3 T
So the magnitude of the magnetic field after the change is 8.0 x 10^-3 T.
Which of the following best describes the relationship between the two variables?
Answers
Answer:
correlation is defined as the statistical association between two variables
Explanation:
a correction exits between two variables when one of them is related to the other in some way
URGENT!!! 50 POINTS NO CHATGPT!
A fisherman notices that his boat is moving up and down periodically without any horizontal motion, owing to waves on the surface of the water It takes a time of 3.00 s for the boat to travel from its highest point to its lowest, a total distance of 0.650 m
mThe fisherman sees that the wave crests are spaced a horizontal distance of 5.90 m apart
Part A
How fast are the waves traveling?
Express the speed v in meters per second using three significant figures.
What is the amplitude A of each wave?
Express your answer in meters using three significant figures.
Answers
Answer:
Part A: [tex]1.97ms^{-1}[/tex] (2 s.f.)
Part B: 0.33m (2 s.f.)
Explanation:
Part A:
Frequency = [tex]\frac{1}{period} = \frac{1}{3}[/tex] Hz
Wavespeed = frequency x wavelength
Wavelength = distance between two crests = 5.90
Freq = 1/3 Hz
Therefore: Wavespeed = 1/3 x 5.90
Wavespeed = 1.967 ms^-1
Part B:
Amplitude = [tex]\frac{peak-to-peak- amplitude }{2}[/tex]
Peak to peak amplitude = 0.65m
Amplitude = 0.65/2 = 0.325m = 0.33m 2sf
The diagram shows the electric field lines due to two charged parallel metal plates. We conclude
that:
a.
an electron at X could have its weight balanced by the electrical force
b.
a proton at X experiences a greater force than if it were placed at Z
c.
the upper plate is positive and the lower plate is negative
d.
a proton at X experiences less force than if it were placed at Z
e.
a proton at X would experience the same force if it were placed at Y
Answers
Based on the given diagram, we can only reasonably conclude statement c, that the upper plate is positive and the lower plate is negative
What is Electric Field?
Electric field is a concept used in physics to describe the influence that an electric charge exerts on other charges in its vicinity. It is defined as the force experienced by a positive test charge placed in the vicinity of an electric charge, divided by the magnitude of the test charge
The upper plate is positive and the lower plate is negative: This statement is a common convention for charged parallel metal plates in a capacitor. The positive plate is usually considered as the plate with electric field lines originating from it (in this case, the upper plate), and the negative plate is usually considered as the plate with electric field lines terminating on it (in this case, the lower plate). So, this statement is likely to be true based on convention.
Learn more about Electric Field from the given link
https://brainly.com/question/14372859
#SPJ1
The attractive electric force between the point charges q and −2q has a magnitude of 2.2 N when the separation between the charges is 1.4 m . k=8.99×109N⋅m2/C2
What is the magnitude of charge q?
Answers
The electric force between two point charges is given by the equation
[tex]F=k*q_1*q_2/r^2[/tex]
What is force?The interaction between two things is measured by the physical quantity known as force. It is a vector quantity, and the sign F is frequently used to denote it. When an object interacts with another object, it feels a push or a pull.
where r is the distance between the charges, q1 and q2 are their magnitudes, and k is the Coulomb constant.
When we enter the problem's specified values, we obtain
[tex]2.2N=8.99*10^9\ N*m^2/C^2*q*-2q/(1.4 m)^2[/tex]
which simplifies to
q = -0.500 N/C.
Thus, the magnitude of charge q is 0.500 N/C.
To learn more about force, visit:
brainly.com/question/12785175
#SPJ1
For number 6 I really can't figure out the answer does anyone know ?
Answers
The factor that leads to loess deposit is when the wind carries fine sediment. That is option C.
What are loess deposits?The loess deposits are those deposits that are usually found at the edge of deserts.
The major factor that causes the formation of loess is the wind because they are entrained, transported, and deposited by the wind.
The fine particles carried by wind contains find grained sediments, organic particles that are capable of forming loess.
Learn more about wind here:
https://brainly.com/question/29801913
#SPJ1
Ann and Bob are carrying an 18.5 kg table that is 2.25 m long. An 8.33 kg box sits on the table 0.750 from Ann. How much lift force does Ann exert? Use 9.80 for gravity.
URGENT
Answers
F = (m1 + m2) * g * d2 / d1
Where F is the lift force, m1 is the mass of the table, m2 is the mass of the box, g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.80 m/s^2), d1 is the total length of the table, and d2 is the distance from Ann to the box.
Plugging in the given values, we get:
F = (18.5 kg + 8.33 kg) * 9.80 m/s^2 * 0.750 m / 2.25 m
F = 40.3125 N
Therefore, Ann exerts a lift force of 40.3125 N.
an election of mass 9.1 × 10^31kg moves with a velocity of 4.2 × 10^7mJs between the cathode and anode of an X-ray tube. Calculate the wavelength.( take Planck's constant, h= 6.6 × 10^ 34 J's)
Answers
The wavelength of the electron is 1.724 × 10^-12 m.
How do we calculate?The wavelength of the electron is found using the de Broglie wavelength formula:
λ = h / p
where λ = wavelength,
h= Planck's constant, a
p = momentum of the electron.
we find the momentum of the electron,
p = m * v
p = (9.1 × 10^-31 kg) * (4.2 × 10^7 m/s)
p = 3.822 × 10^-22 kg m/s
Therefore, wavelength ;
λ = h / p
λ = (6.6 × 10^-34 J s) / (3.822 × 10^-22 kg m/s)
λ = 1.724 × 10^-12 m
Learn more about wavelength at: https://brainly.com/question/10728818
#SPJ1
A 25 kg child plays on a swing having support ropes that are 2.20 m long. A friend pulls her back until the ropes are ăÿÿfrom the vertical and releases her from rest. (a) What is the potential energy for the child just as she is released compared with the potential energy at the bottom of the swing? (b) How fast will she be moving at the bottom of the swing? (c) How much work does the tension in the ropes do as the child swings from the initial position to the bottom?
Answers
U = mgh
where m is the mass of the child, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height above the lowest point (i.e., the bottom of the swing). At the highest point, h = 2.20 m, so:
U_top = mgh = (25 kg)(9.81 m/s^2)(2.20 m) = 544.5 J
At the bottom of the swing, all the potential energy has been converted to kinetic energy, which is given by:
K = (1/2)mv^2
where v is the velocity of the child at the bottom of the swing. Since the swing is released from rest, the initial velocity is zero. Therefore, the kinetic energy at the bottom of the swing is equal to the potential energy at the top of the swing:
K_bottom = U_top = 544.5 J
b) Setting the potential energy at the top of the swing equal to the kinetic energy at the bottom of the swing, we can solve for the velocity:
K_bottom = (1/2)mv^2
544.5 J = (1/2)(25 kg)v^2
v = sqrt(2*544.5 J / 25 kg) = 9.89 m/s
Therefore, the child will be moving at a speed of approximately 9.89 m/s at the bottom of the swing.
c) The work done by the tension in the ropes is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the child as she swings from the initial position to the bottom. Since the child starts from rest, the initial kinetic energy is zero. Therefore, the work done by the tension is equal to the final kinetic energy at the bottom of the swing:
W = K_bottom = (1/2)mv^2 = (1/2)(25 kg)(9.89 m/s)^2 = 1228.3 J
Therefore, the tension in the ropes does 1228.3 J of work as the child swings from the initial position to the bottom.
As a 5.00-kg sample of liquid mercury is cooled into a solid, it liberates 157 kJ of energy. What is the original temperature of the mercury? For mercury, the melting point is 234 K, the heat of fusion is 11.3 kJ/kg,
and the specific heat is 140 J/kg . K.
378 K
690 K
157 K
410 K
Answers
The original temperature of the mercury is 260.6K
Here is how to arrive at temperature of the mercuryTo solve this problem, we can use the formula for the heat released during the solidification of a substance:
Q = m * Lf
where Q is the heat released, m is the mass of the substance, and Lf is the heat of fusion of the substance.
In this case, Q = 157 kJ, m = 5.00 kg, and Lf = 11.3 kJ/kg.
We also need to use the formula for the heat absorbed or released during a temperature change:
Q = m * c * ΔT
where Q is the heat absorbed or released, m is the mass of the substance, c is the specific heat of the substance, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
We can use this formula to calculate the heat released as the mercury cools from its original temperature to its melting point, and then use the formula for solidification to calculate the heat released as the mercury solidifies.
Let T be the original temperature of the mercury.
The heat released as the mercury cools from its original temperature to its melting point is:
Q1 = m * c * (T - 234)
The heat released as the mercury solidifies is:
Q2 = m * Lf
The total heat released is:
Q = Q1 + Q2 = m * c * (T - 234) + m * Lf
Substituting the values given in the problem, we get:
157 kJ = 5.00 kg * 140 J/kg . K * (T - 234) + 5.00 kg * 11.3 kJ/kg
Simplifying and solving for T, we get:
T = 260.6 K
Therefore, the original temperature of the mercury was 260.6 K.
Learn more about Energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/13881533
#SPJ1
50 POINTS!! NO BOTS
A tsunami (tidal wave) traveling across deep water can have a speed of 750 km/h
and a wavelength of 270 km
What is the frequency of such a wave?
Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units
Answers
The frequency of the tsunami wave is estimated at 0.001 Hz
How do we calculate?Frequency is described as the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time
Using the formula for the speed of a wave:
v = λ x frequency
where v is the wave speed, λ is the wavelength, and f_ is the frequency.
frequency = v / λ
Substituting the values given in the problem, we have
frequency = 750 km/h / 270 km = 2.78 h^(-1)
f_ = 2.78 h^(-1) * (3600 s/h) = 1.00 x 10^(-3) s^(-1) or 0.001 Hz
Learn more about frequency at: https://brainly.com/question/254161
#SPJ1
List different type of thermometer in terms of their thermometer properties
Answers
Answer:
Look below.
Thermometric Property ThermometerVolume expansion of a gas Gas thermometer
Volume expansion of a liquid Laboratory or clinical thermometer
Volume expansion of a solid Bi-metallic strip thermometer
Pressure change of a fixed mass of gas Constant – volume gas thermometer
Air passes over the top of an airplane wing at 170 m/s.
Answers
The speed of air passing over an airplane wing is an important factor in determining the lift generated by the wing. The faster the air moves over the wing, the greater the lift that is generated.
What is air ?Air is a mixture of gases that makes up the Earth's atmosphere. It is composed primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), along with small amounts of other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, neon, and helium. The composition of air can vary depending on factors such as altitude, location, and weather conditions.
Air plays a vital role in supporting life on Earth, providing us with the oxygen we need to breathe and helping to regulate the planet's temperature and climate. It also plays an important role in various natural processes, including the water cycle, plant growth, and the formation of weather patterns.
Air is used in a wide range of human activities, including transportation, heating and cooling systems, industrial processes, and combustion for energy production. However, human activities can also contribute to air pollution, which can have negative impacts on human health and the environment.
To know more about Air visit :
https://brainly.com/question/19368011
#SPJ1
A 25 kg child plays on a swing having support ropes that are 2.20 m long. A friend pulls her back until the ropes are ăÿÿfrom the vertical and releases her from rest. (a) What is the potential energy for the child just as she is released compared with the potential energy at the bottom of the swing? (b) How fast will she be moving at the bottom of the swing? (c) How much work does the tension in the ropes do as the child swings from the initial position to the bottom?
Answers
If the sun were more massive, what would happen to Earth’s gravity with the sun?
A. decrease
B. would be infinite
C. would be 0
D. increase
Answers
Answer: d. increase
Explanation:
If the sun were more massive, the gravitational force between the sun and Earth would increase. This means that Earth's gravity with the sun would also increase. Therefore, the correct answer is (D) increase.
The gravitational force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. So, if the mass of one of the objects increases, the gravitational force between them will also increase. In this case, if the mass of the sun were to increase, the gravitational force between the sun and Earth would become stronger, and hence, Earth's gravity with the sun would also increase.
According to this graph, the acceleration
is approximately:
A. 12 m/s²
C. 4 m/s²
Velocity (m/s)
14
12
10
12 2 3 4
Time t (s)
B. 1.5 m/s2
D. 3 m/s2
Help please
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Because you have velocity along the y axis and time along the x axis, this is a velocity v time graph which is an acceleration graph. The slope of the line in this graph IS the acceleration. We can use 2 points and the slope formula to solve for the acceleration:
(0, 0) and (1, 3):
[tex]m=\frac{3-0}{1-0}=3[/tex] m/s squared, choice D.
Emilia is on a swing, as shown below. Positions A,
B, and C are different locations along her swing
path. Assume that the swing has no friction.
Position C is at the same height as positionA.
FAM
Describe the changes in energy as she moves
from point A to B to C
Answers
When Emilia goes from point A to point B, her energy shifts from potential to kinetic, and from kinetic to potential as she moves from point B to point C.
What is energy?Energy is a key idea in physics that describes a system's capacity for work. Energy is a scalar quantity that may be transformed between many different forms and is a measure of a system's capacity to perform work.
Emilia's gravitational potential energy reduces as she goes from point A to point B because she gets closer to the earth. However, when she picks up speed, the conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy causes her kinetic energy to rise. All of Emilia's potential energy has been transformed into kinetic energy at point B.
Emilia's kinetic energy falls as she advances from point B to point C because gravity is working against her motion, slowing her down. However, when she moves farther from the earth, her potential energy rises. Emilia is at her highest point in her swing at point C, when all of her kinetic energy has been transformed back into potential energy.
To know more about energy, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/2409175
#SPJ1
franchising why is it the best option for you as an entrepreneur
Answers
Answer:
ttrockstars
Explanation:
it's math you to be an expert at math thank you